An external link is a link from one site which links to another site not on the same domain.
External links stand in contrast with internal links, which are links pointing to a page on the same domain or subdomain.
Having authoritative external links is one of the most important ranking signals of Google's ranking algorithm.
Understanding External Links
There are two types of external links: Inbound and Outbound links.
Outbound links are connections between your site and another site. Inbound links work in the reverse manner i.e., they are links pointing to your site from another site.
While most SEO specialists focus on the acquisition of backlinks, it is also important to link out to relevant and authoritative sites.
Outbound Links with URL vs Anchor Text
You can create an outbound link using any one of the methods outlined below. Generally external links are created as either raw URLs or they are inserted on top of "anchor text," which is text that links to another resource.
Raw URL outbound link: https://www.google.com/search/howsearchworks/
Outbound link with anchor text: Google's Explanation of How Search Works
How To Create an External Link
How to Create a Link with HTML
While creating external links in HTML, you will need to use the <a> anchor tag. Each tag in HTML has an attribute attached to it. In the case of an anchor tag, the <href> is used to specify the web address of the new page. The general convention for the anchor tag is as follows:
<a href="link address"></a>
By default, the new page that the external link directs to is opened on the same browser page. You can change this setting by specifying that the new link is opened on a target page. The target attribute indicates to the browser whether to open the link in a new tab or window.
Examples of External Links Using HTML
Shown below is an example of HTML syntax for an external link. It has been created using the elements mentioned above.
<a href="link URL">anchor text</a>
In the above example, ahref directs the user to the linked page's web address while the target attribute opens the link in a new page.
Let's consider the following practical example below:
<a href="https://101domain.com"> Welcome to 101domain </a>
The HTML tag above creates a link to the 101domain home page over the "Welcome to 101domain" text.
How to Create a Link with Wordpress
There are two ways to create an external link in a Wordpress website as discussed in this blog article. The first method is to use the Edit as HTML option (highlighted in blue) while creating a new block in the Wordpress editor.
Once you have selected the HTML option, you can work on the block as on a standard HTML file and add tags, explained above, to insert external links to another page or site.
The other method to create external links in Wordpress is to do it directly in a Wordpress editor.
The process is fairly simple—follow the steps outlined below to create an external link in the Wordpress editor.
Note that the steps below pertain to the new Wordpress Block Editor. The steps mostly remain the same, even if the previous version of Wordpress's visual editor is used.
1. Select or highlight the text that you want to link to another site.

2. Choose the hyperlink icon on the Wordpress visual editor. Then, enter the hyperlink URL and use the slide button to specify whether you want the link to open in a new tab. Sliding towards the right will open the link in a new tab.
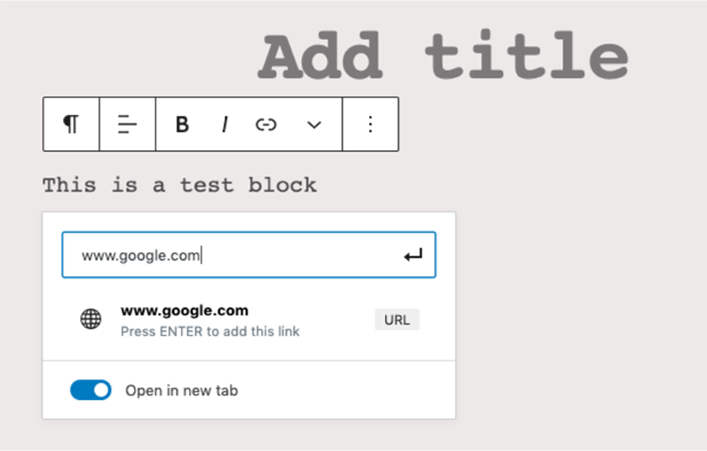
3. Click the Enter icon to insert the link.
Relationship Attributes for External Links
Because Wordpress is a content management system, it automatically adds attributes to the HTML tags specified by its visual editor. These attributes are known as Relationship attributes.
Here are a couple of important relationship attributes. You can download plugins from Wordpress to append or remove these attributes.
rel="noopener" and rel="noreferrer"
Using rel="noopener" is valuable for link security against cross-site hacking to prevent tampering with the originating document. Since there is no impact to performance or SEO, the noopener value should always be added to external links purely for its security merits.
To patch a security vulnerability, Wordpress adds noopener to all links that specify opening in a new window or tab, and should never be removed. In other words, the attribute will be added to HTML code if you slide the Wordpress visual editor button to the right.
The screenshot below shows the attributes as added by Wordpress.

The rel="noreferrer" attribute masks the origin of the referrer. This data is generally available through Google Analytics, which typically displays search traffic location and data on a granular as well as broad level.
But the "noreferrer" attribute conceals the actual source from which the link came, instead displaying it as direct traffic to the website.
Some search specialists have raised concerns that noreferrer could affect SEO rankings. While it does not directly impact SEO, but it can impact your link building and promotion efforts because it prevents reciprocal link attention. Bottomline, it could prevent getting a link back to your website.
The attribute also does not affect affiliate marketing because it passes on affiliate ID information that can be used to tally up marketing efforts.
You can remove the attributes by choosing not to open the link window in a new tab in the visual editor or removing the attributes manually from the code.
rel="nofollow"
rel="nofollow" prevents Google's PageRank algorithm from passing on link juice (or considering the link as a proper SEO reference) to another site. In this way, the target site's search rank remains unaffected by the link.
You may use this attribute for links that you do not trust or suspect of being low-quality.
They are also used to distinguish sponsored links from their organic counterparts. Most large news organizations sites, such as CNN and The New York Times, place nofollow on all of their outbound links.
At first glance, nofollow might seem similar to noreferrer, however the difference between them lies in the fact that nofollow does not pass SEO value to the target site, but the source of the link is displayed to the target site.
In contrast, noreferrer passes SEO value to Google's algorithm, but does not display link origin data to the target site.
As of March 1, 2020, Google has said that, while it will not crawl or index nofollow links, it will treat them as "hints"; meaning, it may choose to crawl them at its own discretion.
Sponsored External Links and User-Generated Content (UGC)
Google has extensive policies outlining its stance on paid links.
The rel="sponsored" attribute was introduced in September 2019 to identify paid links.
This attribute is specifically used to identify external links that are sponsored or link to paid advertorials or sponsored content. Google has not explicitly specified whether this attribute also includes affiliate links.
As in the case of nofollow, Google's PageRank algorithm does not count these links as a referral and, therefore, the target sites do not receive link juice from the referring site.
You can use various plugins to automatically add these attributes to outbound links within Wordpress.
The rel="ugc" attribute refers to user-generated content. This attribute should be added whenever links are created by users, rather than the editor of the site.
For example, the commenting section of a popular article can become a popular forum to generate referral traffic through link placements.
By automatically categorizing these links with the user-generated content attribute, the original site can make sure that it is not allowing users to use its comments section to pass PageRank to their websites.
According to Google, if the user-generated content comes from a trusted contributor on the site, such as a frequent commenter, then it may not be necessary to add this attribute. Wordpress automatically appends the user-generated content attributes to comments on sites.
How to Find Your Site's Outbound and Inbound Links
Inbound links, also known as backlinks, are links from other sites to your site. Websites your site links to are outbound links.
Every inbound link to your site is an outbound link from another site.
You can use the Google Search Console to extract reports for external links and backlinks. Login to Google Search Console using your Google credentials and navigate to the Links section to see a list of external and internal links from and to your site.
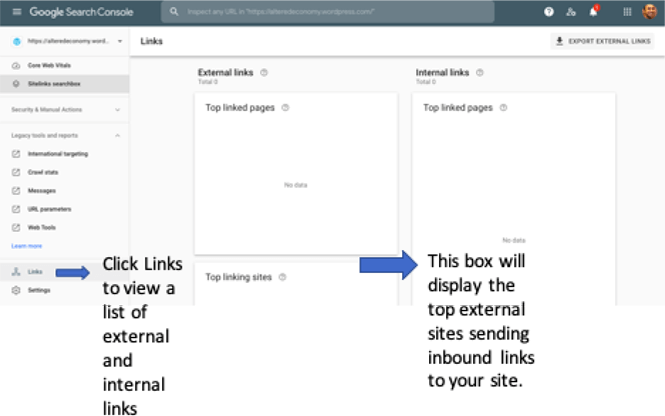
To export data pertaining to backlinks, simply hit the Export External Links button on the top right corner of the console. The top linking sites data contains data pertaining to linking pages and external pages.
However, the list displayed by GSC is not comprehensive because backlink data can be spread across multiple external links.
From the list generated by Google, you also need to identify links that are accurate and trustworthy. Only such links will help increase your site's ranking in Google's search algorithm.
Third-party tools, such as Ahref and SEMrush, are useful to sift bad links from quality ones. These tools crawl your site and list issues with links and SEO practices.
For example, they might list an ineffective or bad quality backlink to your site and you can block it. But they require paid subscriptions.
If you have sufficient knowledge of spreadsheet software and basic SEO practices, you can troubleshoot problematic links on your own by exporting data to Excel or Google Sheets using Google Search Console.
Backlinks can also be disavowed. For example, if a third-party webmaster has built links of low quality into your website to increase its ranking in search results, you can disavow these links by uploading a file for Google on the Disavow Links page (Google sign in required).
Summary
External links are where the domain space and SEO crossover. It is well known that having highly authoritative external links pointing to your website will help its SEO ranking.
To increase the number of inbound links your site receives, it's important to have a short and memorable domain name. This will also give you better domain ranking.
At 101domain, we offer more top-level domains than any other registrar, offering more flexibility and opportunity to perfectly match your business's needs.
While a .com domain will always be a primary staple, consider the other options for a domain name:
Country code top level domain (ccTLD)
New industry-specific generic top level domains
Premium domains
Domain Hacks
